Configuring SPF/DKIM/DMARC
Here are three methods for authenticating your e-mails and thereby reducing abusive e-mail use (spam, phishing, etc.).
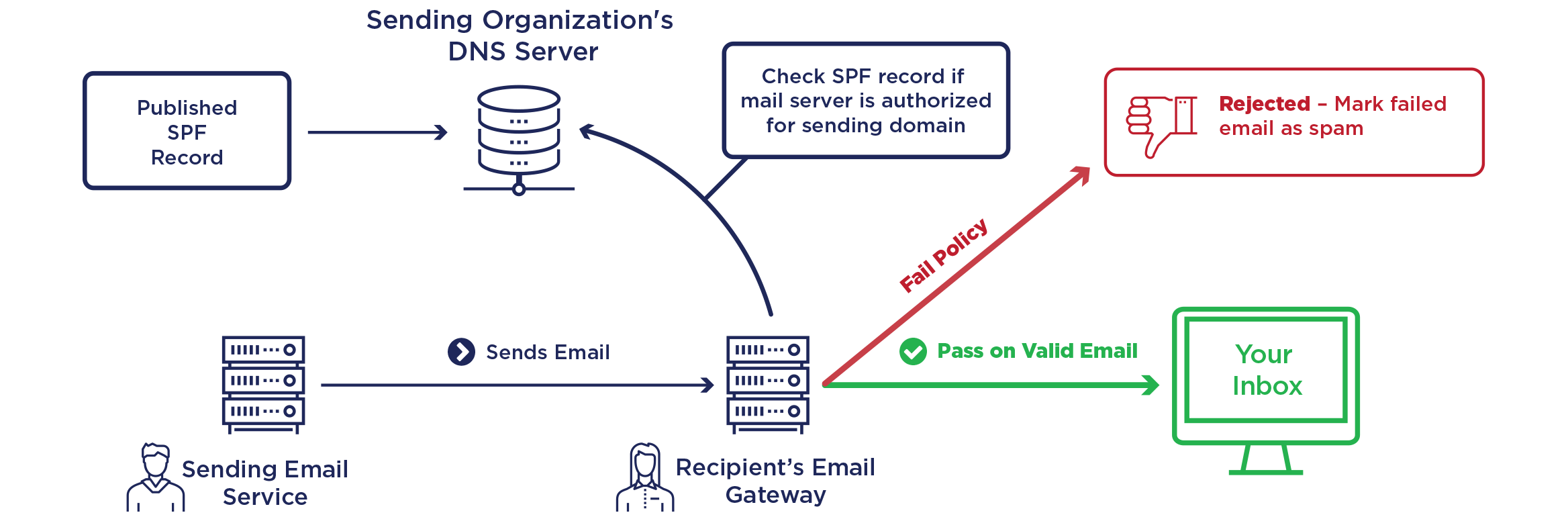
Sender Policy Framework
SPF makes a TXT type DNS request to the sender’s domain ("MAIL FROM" in the message headers) to find out the list of servers allowed to send e-mails and compare it with the IP address of the sender’s server.
Parameters
| Mechanism | |
|---|---|
| ALL | Default result |
| A | An IN A (or AAAA) record that can be resolved as the sender’s address |
| IP4 | IPv4 range |
| IP6 | IPv6 range |
| MX | A Mail eXchanger record pointing to the sender’s address |
| EXISTS | The domain is resolved at any address |
| INCLUDE | An included rule passes the test |
| PTR | The IP address domain corresponds to the specified domain and the latter points to the IP in return |
| Qualifiers | |
|---|---|
| + | Favorable result |
| ? | Neutral result |
| ~ | Slight “SOFTMAIL” failure (e-mail accepted but marked) |
| - | Total failure (e-mail normally rejected) |
| Modifiers | |
|---|---|
| exp=some.example.org | To get the reason for the failure results |
| redirect=some.example.org | To link to a rule record in another domain |
Warning
This technology may have an impact on e-mail redirects as the sender server is not necessarily the e-mail server belonging to the original e-mail sender.
At alwaysdata
A SPF record is created by default and can be found in the DNS records tab for the domain:

include:_spf.alwaysdata.comexplicitly allows our servers to send e-mails,~allsends a slight “SOFTMAIL” failure result for the other sender servers.
If the domain doesn’t use alwaysdata’s DNS servers, you must then, in the DNS service provider, add include:_spf.alwaysdata.com to the SPF registration.
Links
DomainKeys Identified Mail
DKIM is used to authenticate the domain name by adding a signature to all of the outgoing e-mails. Concretely, this works with two keys:
- a private key that is known - and kept secret - from the domain’s mail delivery servers;
- a public key that corresponds to a DNS registration of the
TXTtype.
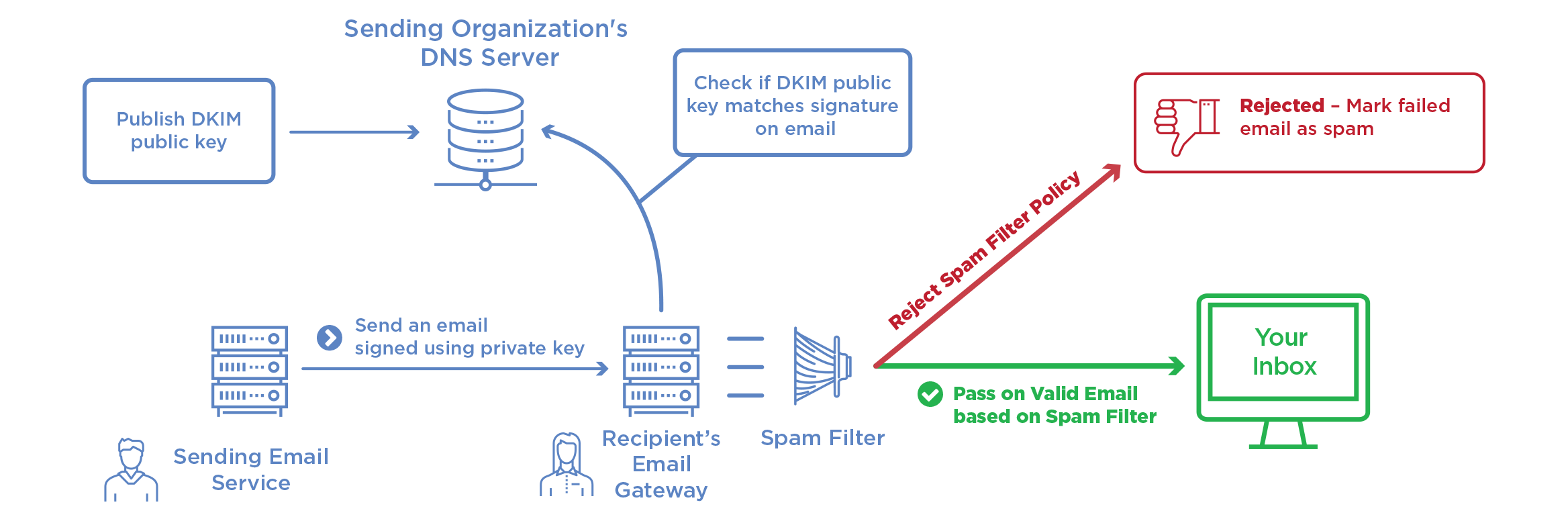
At alwaysdata
A pair of keys is created by default, whose public key (the TXT record) will be found in the DNS Records tab of the domain:
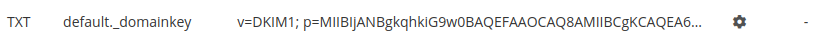
If the domain doesn’t use alwaysdata’s DNS servers, this record must be recopied with your DNS service provider.
It is possible to generate others in Domains > Details of [example.org] - 🔎 > Configuration.
Links
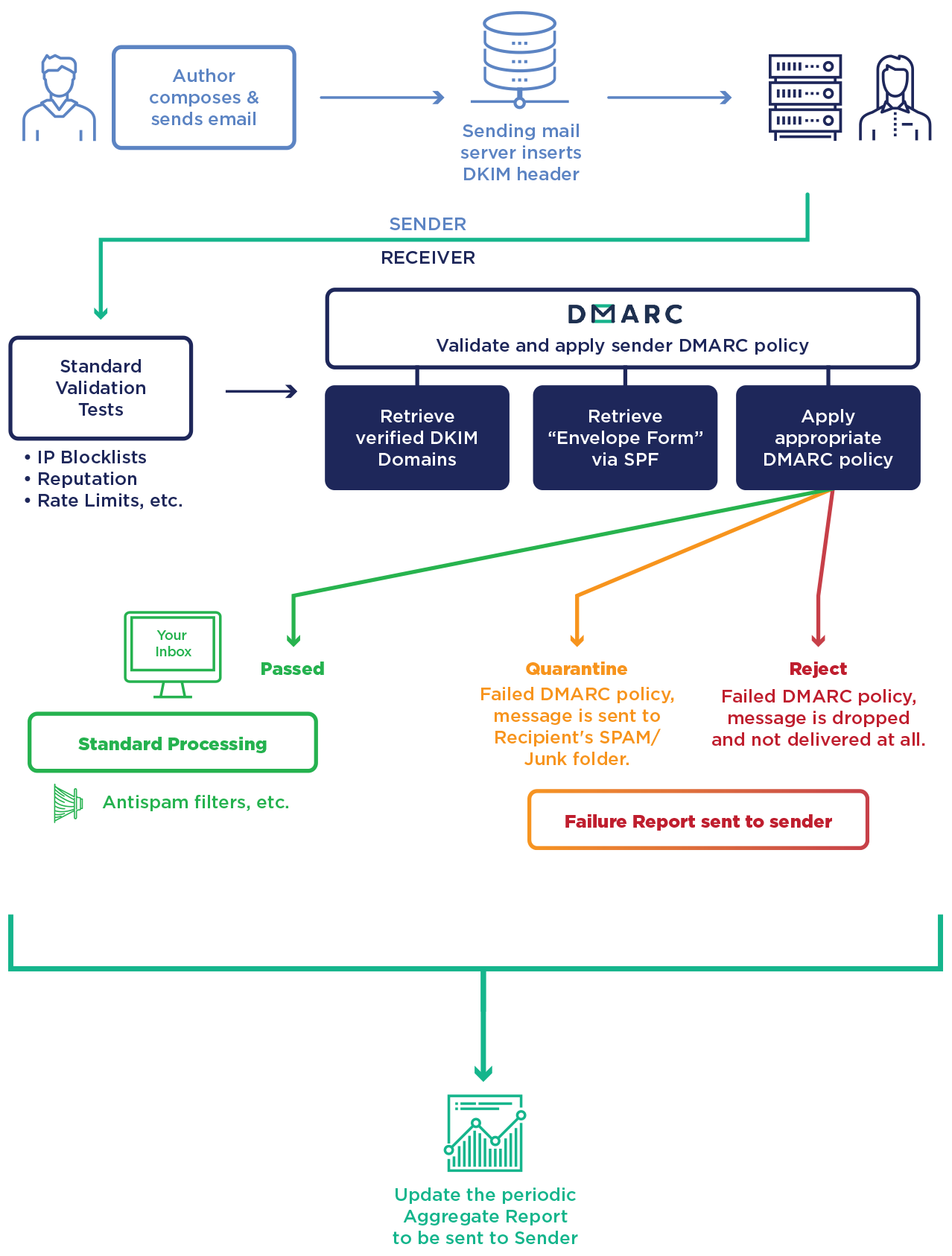
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance
DMARC is a protocol that standardizes authentication by telling the addressees what actions to take should one of the authentication methods fails. It will check that:
- the domain corresponds to the pair of DKIM keys (field d=),
- the sender server is specified in the SPF record for the domain (MAIL FROM),
- the domain is in the e-mail’s FROM field.
Info
To use DMARC, DKIM and SPF must already be implemented.
Parameters
| Variables | |
|---|---|
| v | Protocol version: v=DMARC1 (required) |
| pct | Percentage of messages to filter (default: 100) |
| adkim | Coherency with DKIM |
| s = strict mode - the DKIM signature domain must precisely match the FROM | |
| r = relax mode (default) | |
| aspf | Coherency with SPF (s or r) |
| p | Procedure in case of failure - main domain (required) |
| none = delivers the e-mail normally | |
| quarantine = treats the e-mail as suspect (spam score, flag, etc.) | |
| reject = rejects the e-mail | |
| sp | Procedure in case of failure - subdomain (none, quarantine or reject) |
| ruf | Recipient of the detailed failure reports |
| fo | Conditions for sending a detailed report |
| 1 = DKIM and/or SPF failure | |
| d = DKIM failure | |
| s = SPF failure | |
| 0 = DKIM and SPF failure (default) | |
| rua | Recipients of aggregated failure reports |
To implement it, a TXT DNS record needs to be created. At alwaysdata, you will find it in the DNS records tab of the domain:

Links
Explanatory diagrams reused from Global Cyber Alliance