Configuring Python
[package] and [version] have to be replaced by the name of the package and version to be installed.
Supported versions
| 3.14 |3.13 | 3.12 | 3.11 | 3.10 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.3 |
| 2.7 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.4 |
The default version can be changed from the alwaysdata administration, under Environment > Python. This is the version that is especially used when you start python.
Versions are not necessarily already installed.
Error logs
You can view the error logs in the $HOME/admin/logs/uwsgi/[id].log file where [id] is the identifier for your site, shown in the Web > Sites section.
An extract of these logs is presented in the administration’s interface (Logs - 📄).
Binary to use
You need to always use python (or /usr/bin/python). Never use python3, python2, python2.7 or any other command.
To force the use of a different version of Python other than the default one, define the environment variable PYTHON_VERSION:
$ PYTHON_VERSION=2.7 pythonIn your scripts, use /usr/bin/python as shebang:
#!/usr/bin/pythonTo force the use of a specific version of Python:
#!/usr/bin/eval PYTHON_VERSION=2.7 pythonThe other binaries included in Python (2to3, pep8, pip, pydoc, etc.) work the same way.
Environment
Your Python environment starts off empty, with no ready installed libraries other than the standard library. You can use pip to install packages, this is the standard Python tool:
$ python -m pip install [package]Packages are installed in the standard $HOME/.local directory and they are automatically added to sys.path by Python.
Note that you will need to re-install the packages if you change the major Python version (versions 3.5 and 3.6 are two different major versions, whereas 3.5.1 and 3.5.2 use the same major version).
We recommend using virtual environments if you use a number of different Python applications so that each one has its own separate environment.
With Python 3, use venv:
$ python -m venv myenvWith Python 2, use virtualenv:
$ virtualenv myenvOnce your virtual environment is installed, you can activate it with:
$ source myenv/bin/activateInstalling a package
Install the latest version of a package:
$ python -m pip install [package]You can specify a specific version:
$ python -m pip install [package]==[version]To install a set of packages defined in a requirements.txt file:
$ python -m pip install -r requirements.txtUninstalling a package
$ python -m pip uninstall DjangoInstalling a package with Distutils
You can install a package using Distutils without using pip:
$ python setup.py install --userIf you use a virtual environment, there is no need to specify --user.
WSGI deployment
For a WSGI application to be accessible by the web, you need to add a site in the administration Web > Sites section:

- type: choose Python WSGI,
- application path: the path to your WSGI application.
You can also fill-in a number of optional fields:
- your application’s working directory,
- environment variables to define,
- a specific version of Python to use,
- the virtualenv directory to use.
ASGI deployement
Applications based on the ASGI standard as asynchronouse Python frameworks can use the User program site type in the section Web > Sites. The most popular HTTP server is Uvicorn.
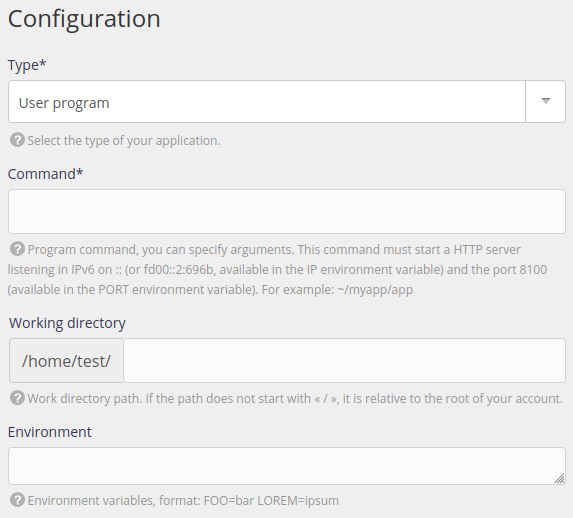
You will have to use the and make the HTTP server listen in IPv6 and on the given port. For example:
- Command:
uvicorn example:app --reload --port $PORT --host $IP
- Deploy a Fastapi (asyncio) application (guide in French written by a user of the platform)