HTTP Cache
The HTTP cache temporarily stores web documents (e.g. HTML pages, CCS documents, images) to reduce the latency induced by the server when it needs to serve up a page and/or reduce its workload.
Concept
When a user attempts to access a page, the corresponding web server will generate a page and send it over the network. Then the cache intercepts the response to store it in its local memory before serving it up to the user.
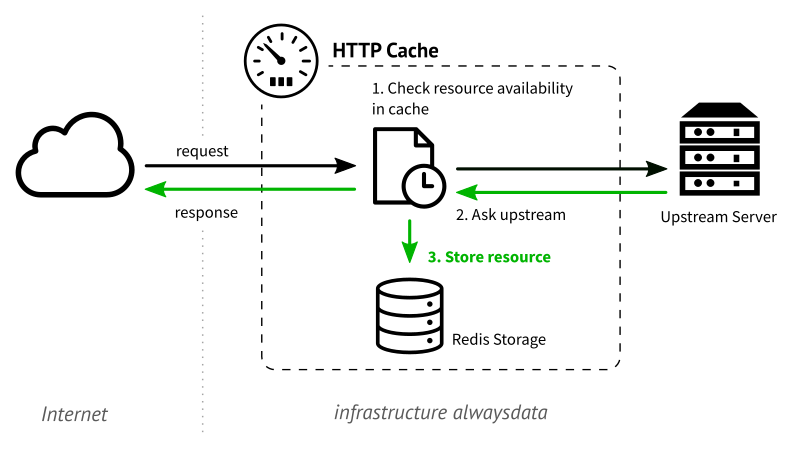
When a request for the same page is sent by the same or another user, the cache will deliver it as it now has a copy of the requested resource. The web server will no longer be queried.
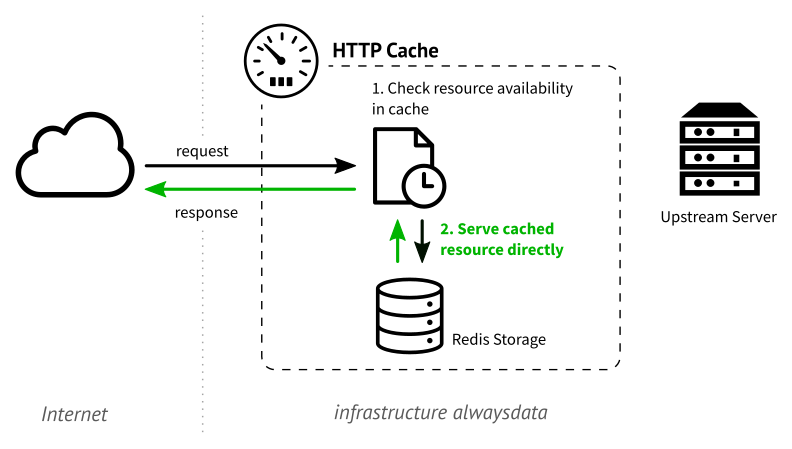
The standard’s specifications are set out in RFC 7234.
Use the HTTP cache
1. Check that your application manages a cache
For the cache to query the upstream to determine if the requested resource has been modified, the application must provide the Etag and/or Last-Modified header.
A response CANNOT be cached if:
- the
Varyheader is*, - the
Content-Typeheader is not present, - the resource
Content-Typeis not one of the following values:text/html,text/xml,text/plain,application/xml,application/html+xml,application/rss+xml,application/rdf+xml,application/atom+xml,text/css,text/javascript; - the
Cache-Controlheader takes one of the following values:private,no-store,no-cache,no-transform; - the
Set-Cookieheader is present, - the
Authorizationheader exists, butCache-Controltakes none of the following values:public,must-revalidate,proxy-revalidate,s-maxage; - The HTTP status code is not one of the following: 200, 203, 204, 206, 300, 301, 404, 405, 410, 414, 501.
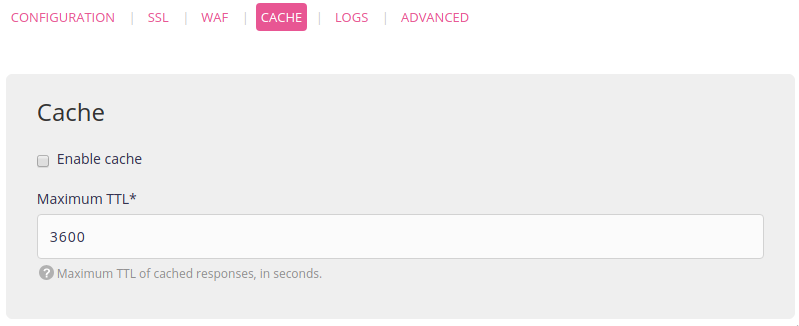
2. Activate the HTTP cache
This is done in Web > Sites > Edit the [site] - ⚙️ > Cache.
Using PURGE
PURGE can be executed in three different ways at alwaysdata:
- by using the full URL of the resource (e.g.
https://test.alwaysdata.net/foo/bar). This will remove the related cache entry and its variations (generated by theVaryheader); - by adding the
X-Cache-Purge-Match: wildcardheader and adding a wildcard to your URL (e.g.https://test.alwaysdata.net/*). This will remove all entries matching the URL template; - adding the
X-Cache-Purge-Match: startswithheader and adding a partial path to your URL (e.g.https://test.alwaysdata.net/foo). This will remove all entries matching the URL template (and thushttps://test.alwaysdata.net/foo/bar).
Note
While the HTTP cache is appropriate in most cases, you can also run Varnish on your alwaysdata account.
Icons: The Noun Project