Scheduled Tasks
Web apps or services sometimes need to periodically run tasks, commands or call up URLs with no user interaction. To manage them you should create a scheduled task.
Our platform is based on Debian and its crontab but allows them to be directly managed from our administration interface - menu Advanced > Scheduled tasks - making their use easier.
Several kinds of information need to be provided:
- the one or more commands that you wish to run or the URLs you wish to request. Email addresses can also be provided to receive error reports1 (separated by a space).
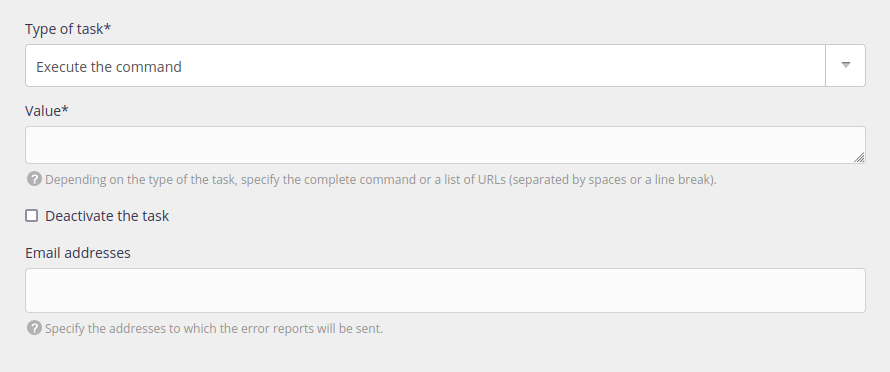
- the SSH environment
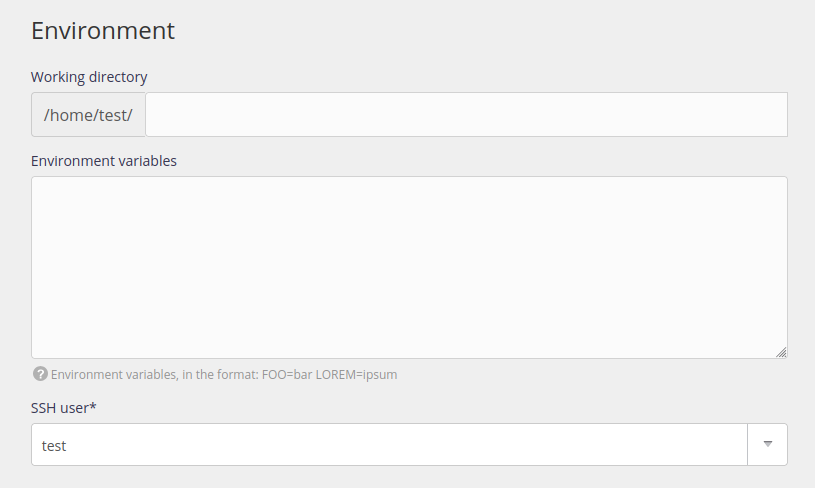
- the task frequency: you can specify a fixed time or an interval
Use scheduled tasks
- If the task is scheduled at a certain frequency but the execution of the previous task is not finished, the current one will be ignored,
- Tasks are started during the set minute. In other words a task scheduled to start every day at 6:30 will start between 6:30:00 and 6:30:59.
- A log is created automatically and is available from the
$HOME/admin/logs/jobs/directory. It gives you the start and end of the task.- An extract of these logs is presented in the administration’s interface (Logs - 📄).
- email addresses provided to receive error reports do not replace these logs.
- Current processes are accessible via the Advanced > Processes > Scheduled Tasks menu.
- For Command type tasks, the language versions used by default are those specified in the Environment menu of the administration interface. It is possible to choose another version using the Environment variables.
Note
If your script needs to allow some IPs, allow these IP adresses ranges.
Public Cloud users:
- The consumption should remain reasonable. If the scheduled task is major processing, then reduce its frequency.
Private Cloud users:
- Even if it is not advisable, they have also access to the
crontab -ecommand. The two systems are separate.
Troubleshooting
source venv/bin/activate && pythonis specific to Bash and can’t function. To replace byvenv/bin/python,- Shortcuts with an @ - examples @hourly or @reboot - are not accepted (non-standard syntax).
Examples
WordPress
Every ten minutes, the WordPress tool starts to run the scheduled tasks:
alwaysdata administration interface:
- value:
php $HOME/wordpress/htdocs/wp cron event run --due-now - frequency: second choice - Every 10 minutes
Equivalent crontab syntax:
*/10 * * * * php $HOME/wordpress/htdocs/wp cron event run --due-nowtt-rss
Refreshing an RSS backend with TT-rss, every day at 10:30:
alwaysdata administration interface:
- value:
php $HOME/tt-rss/update.php --feeds --quiet - frequency: first choice - Every day at 10:30
Equivalent crontab syntax:
30 10 * * * php $HOME/tt-rss/update.php --feeds --quietA report is sent when the return code is different from 0. If the task is not executed, no email is sent. ↩︎